
NEW ADDITION TO RAMSAR SITES
NEW ADDITION TO RAMSAR SITES
Recently, the Meteor Lake at Lonar in Buldhana district of Maharashtra and the Soor Sarovar at Agra have been declared Ramsar sites, a conservation status conferred by International Ramsar Convention on Wetlands. Earlier this year Kabartal Wetland (Bihar) and Asan Conservation Reserve (Uttrakhand) were also designated as Ramsar sites. With latest inclusions, the total number of Ramsar sites in India is 41, the highest in South Asia.
LONAR LAKE & SOOR SAROVAR LAKE

Lonar Lake, also known as Lonar crater, is a notified National Geo-heritage Monument, saline, soda lake, located at Lonar in Buldhana district, Maharashtra, India. Geo-heritage refers to the geological features which are inherently or culturally significant offering insight to earth’s evolution or history to earth science or that can be utilized for education. Lonar Lake was created by an asteroid collision with earth impact during the Pleistocene Epoch. It is one of the four known, hyper-velocity, impact craters in basaltic rock anywhere on Earth. The other three basaltic impact structures are in southern Brazil. It situated in the Deccan Plateau’s volcanic basalt rock, was created by the impact of a meteor 35,000 to 50,000 years ago. The lake is part of Lonar Wildlife Sanctuary which falls under the unified control of the Melghat Tiger Reserve (MTR).
Soor Sarovar Lake is also known as Keetham lake situated within the Soor Sarovar Bird Sanctuary, which was declared as a bird sanctuary in the year 1991. This lake is situated alongside river Yamuna in Agra, Uttar Pradesh. The Soor Sarovar bird sanctuary covered an area of 7.97 sq km. It is today home to more than 165 species of migratory and resident birds. Alongside the Keetham Lake is the Agra Bear Rescue Facility, which is a Sloth bear rescue facility dedicated to rehabilitating previously enslaved 'dancing bears'. The lake has been designated as a protected Ramsar site since 2020. With Ramsar status, the sites will benefit in terms of international publicity and prestige. They will get financial aid through the convention’s grant and also access to expert advice on national and site-related problems.
RAMSAR CONVENTION OF WETLANDS OF INT. IMPORTANCE

The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance especially as Waterfowl Habitat is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands. It is also known as the Convention on Wetlands. It is named after the city of Ramsar in Iran, where the convention was signed in 1971. The Convention came into force in 1975. The Convention’s mission is “the conservation and wise use of all wetlands through local and national actions and international cooperation, as a contribution towards achieving sustainable development throughout the world”. Every three years, representatives of the contracting parties meet as the Conference of the Contracting Parties (COP), the policy-making organ of the convention which adopts decisions (resolutions and recommendations) to administer the work of the convention and improve the way in which the parties are able to implement its objectives. COP12 was held in Punta del Este, Uruguay, in 2015. COP13 was held in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, in October 2018.
THREE PILLARS OF THE CONVENTION ARE:
• Work towards the wise use of all their wetlands.
• Designate suitable wetlands for the list of Wetlands of International Importance (the “Ramsar List”) and ensure their effective management.
• Cooperate internationally on transboundary wetlands, shared wetland systems and shared species.
Montreux Record: It is maintained as part of the Ramsar List. Montreux Record is a register of wetland sites on the List of Wetlands of International Importance where changes in ecological character have occurred, are occurring, or are likely to occur as a result of technological developments, pollution or other human interference.
WHAT ARE THE WETLANDS?
• Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of 1971 defines wetlands as - “Areas of marsh, fen, peat land or water, whether natural or artificial, permanent or temporary, with water that is static or flowing, fresh, brackish or salt, including areas of marine water the depth of which at low tide does not exceed six metres.” In simple terms, a wetland is a land area that is saturated with water, either permanently or seasonally. This definition brings ponds, lakes, estuaries, reservoirs, creeks, mangroves and many more water bodies under the ambit of wetlands.
• Further, wetlands can be categorised into marine (coastal wetlands), estuarine (including deltas, tidal marshes, and mangrove swamps), lacustarine (lakes), riverine (along rivers and streams), and palustarine (‘marshy’– marshes, swamps and bogs) based on their hydrological, ecological and geological characteristics.
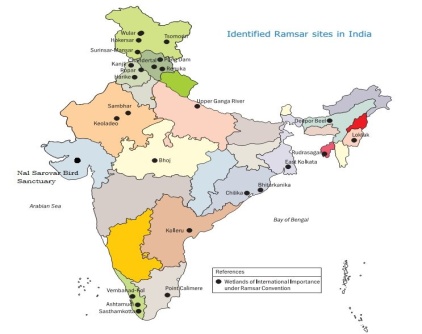
• The wetlands in India are spread over all the 36 States/Union Territories starting from Wular lake in Srinagar, Ashtamudi backwaters lake in Kerala, Loktak lake (only floating national park in the world) in Manipur and Nalsarovar in Gujarat.
• In terms of numbers West Bengal (1.47 lakhs), Uttar Pradesh (1.2 lakhs) are the two States in which wetlands are more than above 1 lakh. These States are followed by Odisha and Madhya Pradesh that have 78 and 62 thousand wetlands respectively.
• In terms of the proportion of the geographical area, Gujarat has the highest proportion (17.5 percent) and Mizoram has the lowest proportion (0.66 percent) of the area under wetlands. Among UTs in India, Lakshadweep has the highest proportion (around 96 percent) and Chandigarh has the least proportion (3 percent) of geographical area under wetlands.
OTHER INITIATIVES FOR THE CONSERVATION OF WETLANDS
• National Wetland Conservation Programme (NWCP): It was launched in 1985 to enable conservation and wise use of wetlands in the country so as to prevent their further degradation.
• The Central Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules: They were notified for the first time in 2010 for better management and regulation of wetlands across the country. It saw the formation of Central Wetlands Regulatory Authority (CWRA) whose term ended on 31 March 2015 and it wasn’t reconstituted since then.
• National Environment Policy 2006: Recognizing the importance of wetlands, it calls for developing a national inventory of such wetlands and implementing a wide spectrum of policies and plans for wetland conservation and their Environmental impact assessment (EIA).
• National Plan for Conservation of Aquatic Ecosystems (NPCA): It was unveiled in 2015 to provide for policy framework and support to State Governments for integrated management of wetlands. This initiative was launched by merging two separate Centrally Sponsored Schemes (CSS), namely the National Wetlands Conservation Programme (NWCP) and the National Lake Conservation Plan (NLCP).
• The 2nd of February each year is World Wetlands Day, marking the date of the adoption of the convention on 2 February 1971. Established to raise awareness about the value of wetlands for humanity and the planet, WWD was celebrated for the first time in 1997 and has grown remarkably since then.
QUESTIONS (1-5)
Q.1 Which of the following two lakes is the new addition to Ramsar Site (Nov. 2020) and granted the status of International importance?
A. Loktak lake & Lonar Lake
B. Sambhar Lake & Kolleru Lake
C. Lonar Lake & Soor Sarovar Lake: ANSWER
D. Soor Sarovar Lake & Rudra Sagar Lake
Q.2 After the addition of two new Wetlands. What is the total number of Ramsar sites in India which is also the highest in South Asia?
A. 27
B. 29
C. 37
D. 41: ANSWER
Q.3 The place Ramsar of “Ramsar convention” is situated in which of the following countries?
A. France
B. Iran: ANSWER
C. Britain
D. Russia
Q.4 When was India’s first National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) launched?
A. 2010
B. 2008: ANSWER
C. 2001
D. 2006
Q.5 On which of the following dates does the World's Wetlands Day is celebrated marking the date of the adoption of the Ramsar convention?
A. 2nd of February: ANSWER
B. 12th of June
C. 16th of November
D. 5th of December













jgpmyecjbq
Latest News on Education & LAW Exams Blogs | Success Mantra [url=http://www.g96w1ni72it21811t4uzl3u078gcb5nts.org/]ujgpmyecjbq[/url] <a href="http://www.g96w1ni72it21811t4uzl3u078gcb5nts.org/">ajgpmyecjbq</a> jgpmyecjbq http://www.g96w1ni72it21811t4uzl3u078gcb5nts.org/
tcfqtrltbh
Latest News on Education & LAW Exams Blogs | Success Mantra <a href="http://www.g5k0953kl5w5wk7cxrrzj23i98973rx1s.org/">atcfqtrltbh</a> [url=http://www.g5k0953kl5w5wk7cxrrzj23i98973rx1s.org/]utcfqtrltbh[/url] tcfqtrltbh http://www.g5k0953kl5w5wk7cxrrzj23i98973rx1s.org/
zemtnnfhtg
Latest News on Education & LAW Exams Blogs | Success Mantra <a href="http://www.gmzd12p38k430b6mrer1x0vr22196h8bs.org/">azemtnnfhtg</a> zemtnnfhtg http://www.gmzd12p38k430b6mrer1x0vr22196h8bs.org/ [url=http://www.gmzd12p38k430b6mrer1x0vr22196h8bs.org/]uzemtnnfhtg[/url]
jrjnvmlft
Latest News on Education & LAW Exams Blogs | Success Mantra <a href="http://www.gz27jh55k92fwozj8u46h97773m7rj9rs.org/">ajrjnvmlft</a> jrjnvmlft http://www.gz27jh55k92fwozj8u46h97773m7rj9rs.org/ [url=http://www.gz27jh55k92fwozj8u46h97773m7rj9rs.org/]ujrjnvmlft[/url]
gdtxhqzhvq
Latest News on Education & LAW Exams Blogs | Success Mantra [url=http://www.gq86k3sa73bq7z46pw9cj00k41ut85x5s.org/]ugdtxhqzhvq[/url] gdtxhqzhvq http://www.gq86k3sa73bq7z46pw9cj00k41ut85x5s.org/ <a href="http://www.gq86k3sa73bq7z46pw9cj00k41ut85x5s.org/">agdtxhqzhvq</a>